
Cover legend: Rhopalosiphum padi aphids feeding on
Epichloë-symbiotic cool-season grass.
Image credit: Benjamin Fuchs
PLANT PHYSIOLOGY:河南大学解析调控植物耐受盐胁迫的新机制
SALT OVERLY SENSITIVE1 (SOS1)是植物耐受盐胁迫的关键组分。本研究发现C-type Cyclin1;1 (CycC1;1)通过干扰WRKY75介导的对SOS1的转录调控作用而负调控植物对盐胁迫的耐受性。
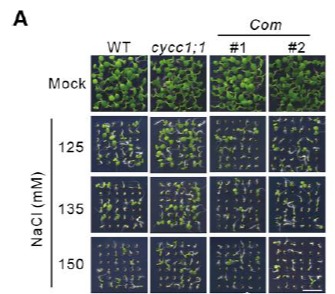
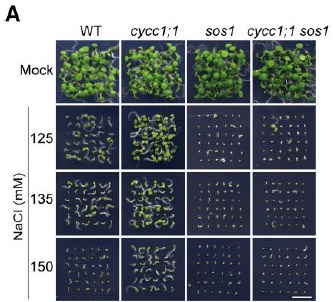
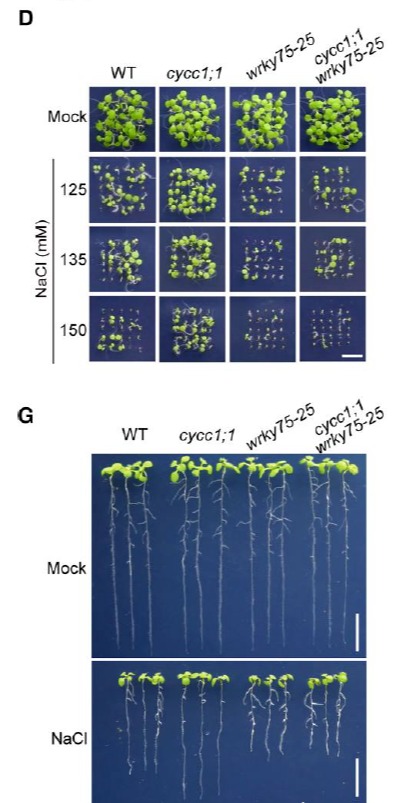
沉默CycC1;1 可以促进SOS1的表达以及提高拟南芥对盐胁迫的耐受性, CycC1;1通过占据SOS1的启动子序列来干扰RNA polymerase II的作用。在cycc1;1 mutant中引入SOS1突变可以降低cycc1;1 mutant对盐胁迫的耐受性,这证实了cycc1;1 mutant对盐胁迫的耐受性是通过影响SOS1实现的。
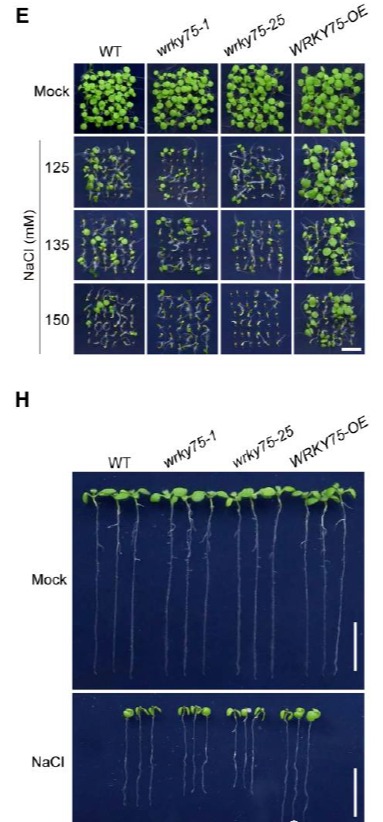
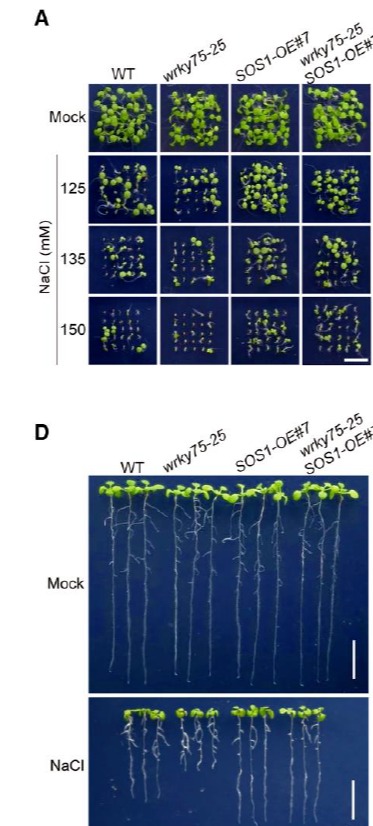
在蛋白水平上CycC1;1与transcription factor WRKY75互作抑制了WRKY75对靶基因表达的调控能力, WRKY75可以结合到SOS1的启动子上来诱导SOS1的表达。与 cycc1;1 mutant相反, wrky75 mutant中SOS1的表达被抑制,同时对盐胁迫的耐受性也显著降低,而过表达SOS1可以挽救wrky75对盐胁迫的敏感型。
小结:本研究揭示了一个在转录水平上调控拟南芥盐胁迫响应组分SOS1的一个调控模块 CycC1;1-WRKY75.
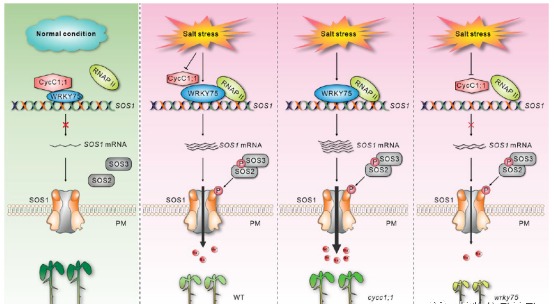
A proposed model showing the mechanism of CycC1;1–WRKY75 complex-mediated transcriptional regulation of SOS1 in response to different salinity conditions in Arabidopsis. Under the normal condition, CycC1;1 interacts with WRKY75 to form a transcriptional repression complex that inactivates SOS1 expression by interfering RNAP II occupancy on the promoter of SOS1 in WT seedlings. When plants are subjected to high salinity stress, the expression of CycC1;1 is suppressed while WRKY75 expression is stimulated, leading to increased recruitment of RNAP II to the SOS1 promoter, thereby activating SOS1 expression and enhancing salt tolerance in WT seedlings. When CycC1;1 is disrupted in the cycc1;1 mutant, WRKY75 transcriptional activation of SOS1 is further enhanced under high salinity conditions, thus leading to higher salt stress tolerance in the mutant than in the WT. In contrast to the cycc1;1 mutant, the wrky75 mutant has impaired salt-induced SOS1 transcription and thus attenuated salt stress tolerance. WT, wild-type; PM, plasma membrane; cycc1;1, CycC1;1 loss-of-function mutant; wrky75, WRKY75 loss-of-function mutant.
原文:CycC1;1–WRKY75 complex-mediated transcriptional regulation of SOS1 controls salt stress tolerance in Arabidopsis
![]() 地址:中国 河南 郑州.明理路北段379号 邮编:450046
地址:中国 河南 郑州.明理路北段379号 邮编:450046![]() 总机号码:0371—22868833
总机号码:0371—22868833